Unlocking The Secrets Of The Desert Biome Food Chain
Alright folks, gather around because we're diving deep into the wild and fascinating world of the desert biome food chain. Now, you might be thinking, "What's so special about a bunch of sand and scorpions?" But trust me, this ecosystem is packed with drama, survival tactics, and some of the coolest creatures on the planet. The desert biome food chain isn't just a random list of animals eating each other—it's a delicate balance that keeps the entire ecosystem alive and kicking. So, buckle up, because we're about to unravel the mysteries of this incredible desert life cycle.
Let's start with the basics. The desert biome food chain is like a giant puzzle where every piece matters. From tiny plants to massive predators, each organism plays a crucial role in keeping the desert thriving. Think of it as nature's version of a reality show, where survival is the ultimate goal. But here's the twist—desert creatures have to deal with extreme heat, scarce water, and limited resources. So, how do they pull it off? Stick around, and we'll break it down step by step.
Now, if you're still wondering why the desert biome food chain is so important, let me drop a quick fact. Deserts cover about one-third of the Earth's land surface, making them one of the largest ecosystems on the planet. And guess what? Despite the harsh conditions, they're teeming with life. From cacti and shrubs to lizards and birds of prey, every living thing in the desert has adapted in mind-blowing ways to survive. So, whether you're a biology buff or just curious about nature's hidden wonders, this article's got you covered.
- Meet All Of Michael Jacksons Siblings The Story Behind The King Of Poprsquos Family
- Tulsa Health Department Food Handlers Permit Your Ultimate Guide To Staying Compliant
What Makes the Desert Biome Unique?
Before we dive into the food chain, let's take a moment to appreciate what makes the desert biome so extraordinary. Picture this: vast stretches of golden sand, rocky landscapes, and an eerie silence that's broken only by the occasional rustle of a snake or the flutter of wings. But don't let the calm fool you—this place is a hotbed of activity. The desert biome is defined by its extreme temperatures, minimal rainfall, and sparse vegetation. Yet, life finds a way to flourish in these challenging conditions.
Key Characteristics of the Desert Biome
Here are some of the standout features that make the desert biome unique:
- Low precipitation: Most deserts receive less than 25 cm of rain annually.
- Extreme temperatures: Days can be scorching hot, while nights drop to freezing cold.
- Sparse vegetation: Plants like cacti and succulents have adapted to store water and survive the dry climate.
- Specialized wildlife: Animals in the desert have evolved incredible adaptations to cope with the heat and lack of water.
These factors create the perfect stage for the intricate dance of the desert biome food chain. Each organism has its own role to play, and the slightest disruption can throw the entire ecosystem out of balance.
- Low Salt Fast Food Items Your Guide To Healthier Eating On The Go
- Palm From Hxh The Ultimate Guide To Her Abilities Personality And Role In The Series
Producers: The Foundation of the Desert Biome Food Chain
Every food chain starts with producers, and in the desert biome, these are the plants that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Now, you might be thinking, "How do plants survive in such a dry environment?" Well, desert plants have some seriously impressive tricks up their sleeves. They've evolved to store water, reduce water loss, and even grow deep roots to tap into underground water sources.
Common Desert Plants
Take a look at some of the superstar producers in the desert biome:
- Cacti: These spiky wonders can store water in their thick stems and have shallow roots to absorb rain quickly.
- Succulents: Similar to cacti, succulents are masters of water conservation.
- Creosote Bush: This hardy shrub can survive for years without water and produces small, fragrant flowers.
These plants not only provide food and shelter for desert animals but also help stabilize the soil and prevent erosion. Without them, the entire food chain would collapse like a house of cards.
Primary Consumers: The Herbivores of the Desert
Next up in the desert biome food chain are the primary consumers—herbivores that munch on plants to survive. These animals have adapted to the desert's harsh conditions by developing unique strategies to conserve water and energy. Some even get all the moisture they need from the plants they eat. Cool, right?
Meet the Herbivores
Here are a few primary consumers you might find in the desert:
- Desert Tortoise: This slow-moving reptile feeds on grasses, flowers, and cacti. It can store water in its bladder for months.
- Kangaroo Rat: These tiny rodents are masters of water conservation. They get all the moisture they need from the seeds they eat and rarely drink water.
- Jackrabbit: With their long ears for heat regulation, jackrabbits graze on desert plants and can survive in extreme temperatures.
Primary consumers are the link between producers and secondary consumers, ensuring that energy flows smoothly through the food chain.
Secondary Consumers: The Carnivores and Omnivores
Now we're getting to the meat-eaters—or should I say, the insect-eaters, lizard-eaters, and bird-eaters. Secondary consumers in the desert biome include carnivores that prey on smaller animals and omnivores that eat both plants and animals. These creatures are the middlemen of the food chain, keeping the population of primary consumers in check.
Top Secondary Consumers
Let's meet some of the coolest secondary consumers in the desert:
- Desert Fox: These clever hunters feed on rodents, insects, and small birds. They have excellent hearing to locate prey.
- Rattlesnake: Known for their venomous bite, rattlesnakes ambush rodents and other small animals.
- Roadrunner: This speedy bird snacks on lizards, snakes, and insects, using its agility to catch prey.
Secondary consumers play a vital role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. Without them, herbivore populations could spiral out of control, leading to overgrazing and habitat destruction.
Tertiary Consumers: The Apex Predators
At the top of the desert biome food chain are the tertiary consumers—apex predators that rule the desert with strength and cunning. These animals have few natural enemies and are the ultimate hunters in their environment. But don't let their tough exterior fool you—they still face challenges like food scarcity and extreme weather.
Meet the Apex Predators
Here are some of the most fearsome tertiary consumers in the desert:
- Coyote: These versatile hunters eat everything from insects to deer. They're opportunistic and can adapt to changing conditions.
- Bobcat: With their sharp claws and stealthy movements, bobcats prey on rabbits, rodents, and birds.
- Eagle: Soaring high above the desert, eagles use their incredible vision to spot prey from miles away.
Apex predators are the final link in the food chain, ensuring that energy is transferred efficiently through the ecosystem. They also help control the populations of secondary consumers, preventing overpopulation and imbalance.
Decomposers: The Unsung Heroes of the Desert
Let's not forget the decomposers—the organisms that break down dead plants and animals, recycling nutrients back into the soil. Without decomposers, the desert biome would be overrun with waste, and the food chain would grind to a halt. These unsung heroes might not be glamorous, but they're essential to the ecosystem's health.
Who Are the Decomposers?
Here are some of the key decomposers in the desert:
- Scavenger Beetles: These insects feast on dead animals, breaking them down into smaller pieces.
- Fungi: Certain types of fungi grow on decaying plant matter, converting it into nutrients for the soil.
- Bacteria: Microscopic bacteria play a crucial role in breaking down organic material and releasing nutrients.
Decomposers might be small, but they have a big impact on the desert biome food chain. By recycling nutrients, they ensure that the cycle of life continues uninterrupted.
The Importance of the Desert Biome Food Chain
So, why does the desert biome food chain matter? Well, it's not just about keeping animals fed—it's about maintaining the health of the entire ecosystem. Each organism, from the tiniest bacteria to the largest predator, contributes to the balance of the desert biome. When one piece of the puzzle is removed, the entire system can collapse.
For example, if a disease wipes out a population of primary consumers, the plants they eat might grow unchecked, leading to overgrazing and habitat destruction. Or, if an apex predator is hunted to extinction, the populations of secondary consumers could explode, throwing the food chain into chaos. The desert biome food chain is a delicate web, and every organism has a role to play.
Threats to the Desert Biome Food Chain
Unfortunately, human activities and climate change are putting the desert biome food chain at risk. Habitat destruction, pollution, and overgrazing are just a few of the threats facing this fragile ecosystem. As temperatures rise and rainfall patterns shift, desert creatures are being forced to adapt—or perish.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protecting the desert biome food chain. By preserving natural habitats, reducing pollution, and promoting sustainable practices, we can help ensure that this incredible ecosystem continues to thrive for generations to come.
Conclusion: Why You Should Care About the Desert Biome Food Chain
And there you have it—a deep dive into the fascinating world of the desert biome food chain. From the spiky cacti to the speedy roadrunners, every organism in this ecosystem plays a vital role in maintaining balance and harmony. The desert might seem like a barren wasteland, but it's actually a vibrant tapestry of life, full of resilience and ingenuity.
So, what can you do to help? Start by learning more about the desert biome and the incredible creatures that call it home. Support conservation efforts, reduce your carbon footprint, and spread the word about the importance of protecting our planet's diverse ecosystems. Together, we can make a difference and ensure that the desert biome food chain remains strong and vibrant.
And hey, don't forget to share this article with your friends and family. The more people know about the desert biome food chain, the better equipped we'll be to protect it. So, what are you waiting for? Get out there and start making a difference!
Table of Contents
- What Makes the Desert Biome Unique?
- Producers: The Foundation of the Desert Biome Food Chain
- Primary Consumers: The Herbivores of the Desert
- Secondary Consumers: The Carnivores and Omnivores
- Tertiary Consumers: The Apex Predators
- Decomposers: The Unsung Heroes of the Desert
- The Importance of the Desert Biome Food Chain
- Threats to the Desert Biome Food Chain
- Conclusion: Why You Should Care About the Desert Biome Food Chain
- Pirates Of The Caribbean Calypso The Enchanting Myth That Fuels Adventure
- What Is Jaspers Power Unleashing The Hidden Potential
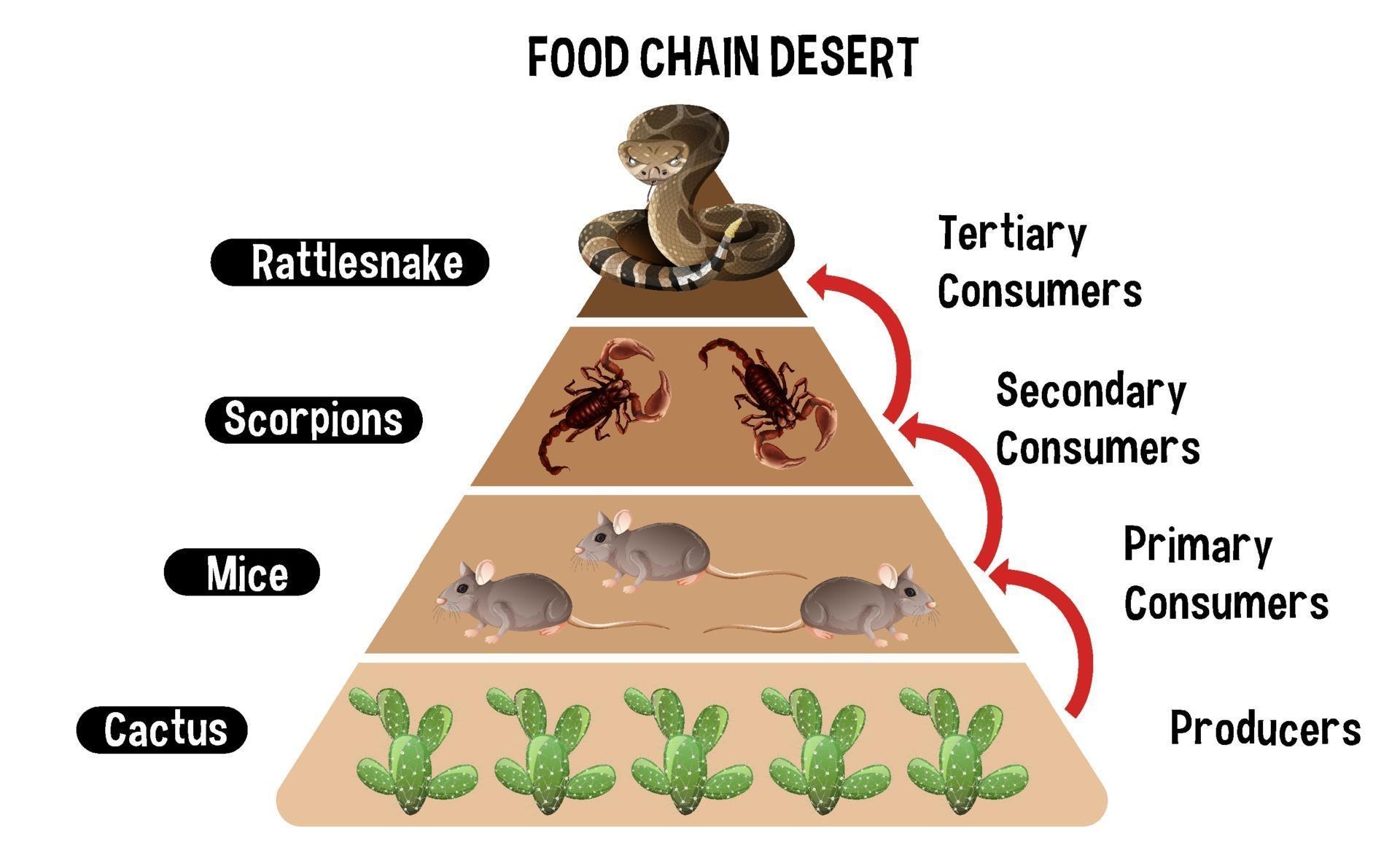
Diagram showing Desert food chain for education 2379595 Vector Art at
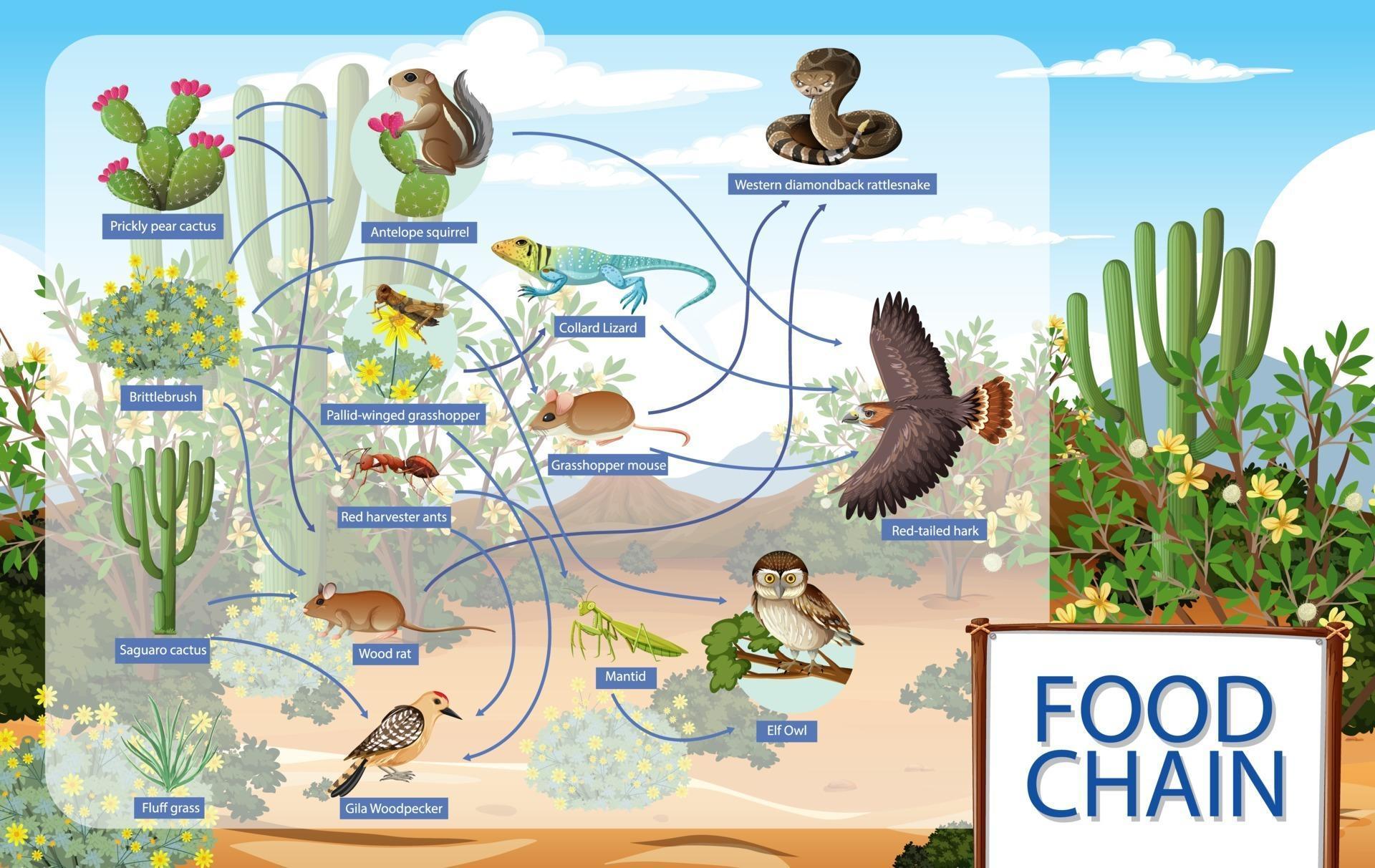
Diagram showing desert animals food chain 2952865 Vector Art at Vecteezy

Desert Food Chains Foldable Kids' Craft Snow Globe Food Web