Is Fast Food Considered Retail? The Ultimate Breakdown
Fast food has become a global phenomenon, and its influence on our daily lives is undeniable. If you’ve ever wondered whether fast food is considered retail, you’re not alone. This question touches on the intersection of commerce, convenience, and consumer behavior. So, buckle up, because we’re diving deep into this topic and shedding light on everything you need to know. Whether you’re a business owner, student, or just curious, this article will answer all your burning questions.
Fast food is more than just burgers and fries; it’s an industry that generates billions of dollars annually. From McDonald’s to Burger King, these brands have redefined what it means to serve food quickly and efficiently. But is fast food really retail? The answer might surprise you. Stick around as we explore the nuances of this fascinating subject.
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let’s clear the air. This article isn’t just another surface-level discussion. We’re breaking down the concept of fast food as retail, exploring its impact on the economy, and examining how it fits into the broader retail landscape. So, grab a snack (maybe not fast food, though), and let’s get started!
- Who Won Cnn Unveiling The Untold Story Behind The Media Giants Triumphs
- Elon Musk Buying Hasbro The Inside Scoop You Need To Know
What Exactly is Retail?
To understand whether fast food is considered retail, we first need to define what retail actually means. In simple terms, retail refers to the sale of goods or services directly to consumers. It’s the final step in the supply chain, where businesses sell products or services to end-users. Retail encompasses everything from clothing stores to electronics shops, and yes, even fast food outlets.
Retailers operate in various formats, including brick-and-mortar stores, online platforms, and even vending machines. The key characteristic of retail is that it involves direct interaction between the seller and the buyer. Whether you’re purchasing a pair of shoes or grabbing a quick bite, the essence of retail remains the same: providing products or services that meet consumer needs.
Now, here’s the kicker: fast food fits neatly into this definition. When you walk into a fast food restaurant, you’re engaging in a retail transaction. You’re buying a product (food) directly from the seller (the restaurant). So, yes, fast food is indeed considered retail. But there’s more to it than meets the eye, and we’ll explore that in the sections below.
- Warren Greys Anatomy Unveiling The Intriguing World Of A Medical Drama Legend
- Was Robin Williams Married Unveiling The Love Life Of A Legendary Actor
Fast Food: The Retail Powerhouse
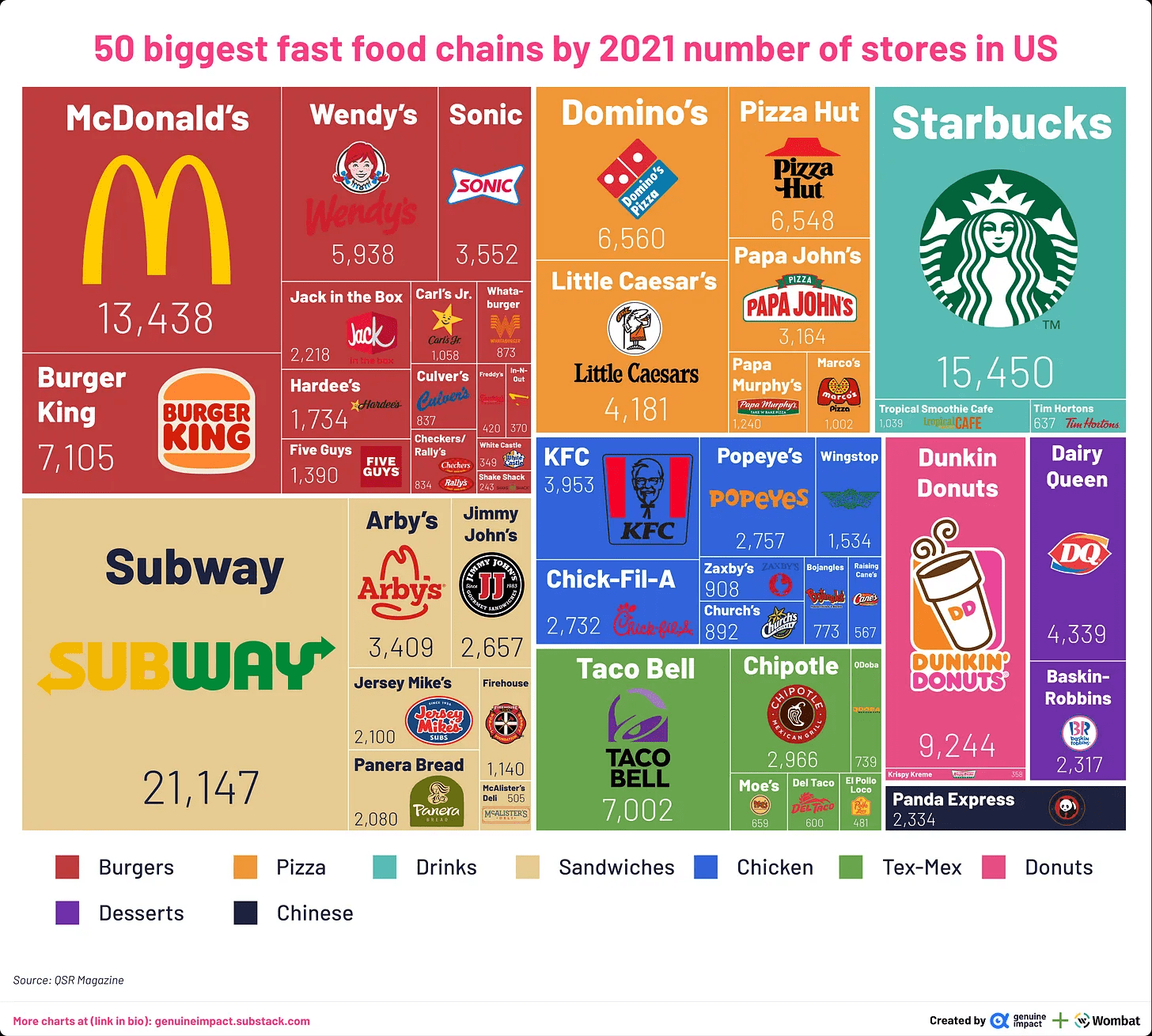
Fast food isn’t just a convenient meal option; it’s a retail powerhouse that dominates the global market. Brands like McDonald’s, KFC, and Starbucks have built empires by mastering the art of retail. They’ve created an environment where customers can walk in, place an order, and leave with their food in minutes. This level of efficiency is what sets fast food apart from other forms of dining.
But what makes fast food so successful as a retail model? Let’s break it down:
- Convenience: Fast food is all about speed and accessibility. Customers can get their meals quickly, making it the perfect choice for busy lifestyles.
- Consistency: Whether you’re in New York or Tokyo, a Big Mac tastes the same. This consistency builds trust and loyalty among customers.
- Branding: Fast food brands invest heavily in marketing and branding. Their logos, slogans, and mascots are instantly recognizable, creating a strong retail presence.
- Technology: Modern fast food chains leverage technology to enhance the customer experience. From digital menus to mobile ordering, they’re always one step ahead.
These factors contribute to the success of fast food as a retail business. But don’t just take our word for it. According to Statista, the global fast food market was valued at over $600 billion in 2022, proving its significance in the retail world.
How Does Fast Food Fit Into the Retail Landscape?
Fast food is a unique player in the retail landscape. While traditional retailers focus on selling tangible goods, fast food combines product and service delivery. This hybrid model allows fast food chains to offer more than just food; they provide an experience.
Let’s take a closer look at how fast food fits into the retail ecosystem:
1. Brick-and-Mortar Stores
Fast food restaurants are a staple of the brick-and-mortar retail scene. They occupy prime locations in malls, airports, and high-traffic areas, making them easily accessible to consumers. These physical stores serve as the backbone of the fast food industry, providing a space for customers to dine in or take out.
2. Online Retail
With the rise of digital technology, fast food has embraced online retail like never before. Customers can now place orders through mobile apps, websites, and even third-party delivery platforms. This shift has expanded the reach of fast food chains, allowing them to cater to a wider audience.
3. Experiential Retail
Fast food isn’t just about the food; it’s about the experience. Brands are increasingly focusing on creating immersive environments that appeal to customers. From themed restaurants to interactive menus, fast food chains are redefining what it means to dine out.
By adapting to changing consumer trends, fast food has solidified its place in the retail landscape. It’s no longer just a meal option; it’s a lifestyle choice.
Is Fast Food Retail Different From Other Retail Sectors?
While fast food shares many similarities with other retail sectors, it also has its own unique characteristics. Let’s explore how fast food differs from traditional retail:
- Product Offering: Fast food primarily sells food and beverages, whereas traditional retailers focus on tangible goods like clothing or electronics.
- Customer Interaction: Fast food transactions are often quick and impersonal, compared to the more personalized service offered by other retailers.
- Supply Chain: Fast food relies heavily on a streamlined supply chain to ensure consistency and quality across all locations.
- Marketing Strategies: Fast food brands use aggressive marketing tactics to stay ahead of the competition, often targeting younger audiences through social media and influencers.
Despite these differences, fast food still operates under the same fundamental principles of retail. It’s all about meeting consumer needs and delivering value.
The Economic Impact of Fast Food as Retail
Fast food’s influence on the economy cannot be overstated. As a retail sector, it generates billions of dollars in revenue and employs millions of people worldwide. Let’s examine the economic impact of fast food:
1. Job Creation
Fast food restaurants are a major source of employment, providing jobs for people of all ages and skill levels. From entry-level positions to management roles, the industry offers a wide range of opportunities.
2. Contribution to GDP
The fast food industry contributes significantly to the global GDP. In the United States alone, fast food generates over $200 billion annually, making it one of the largest retail sectors.
3. Supply Chain Impact
Fast food relies on a vast network of suppliers, distributors, and farmers to keep its operations running smoothly. This supply chain creates additional economic opportunities and supports other industries.
By analyzing these factors, it’s clear that fast food plays a vital role in the global economy. Its impact extends far beyond the food itself, touching every aspect of retail and commerce.
Challenges Facing Fast Food as Retail
Like any retail sector, fast food faces its fair share of challenges. From changing consumer preferences to rising competition, the industry must constantly adapt to stay relevant. Here are some of the biggest challenges facing fast food as retail:
1. Health Concerns
With growing awareness of health and wellness, consumers are becoming more conscious of their food choices. Fast food chains are under pressure to offer healthier options while maintaining their signature taste.
2. Labor Costs
As minimum wage laws change and labor costs rise, fast food businesses must find ways to remain profitable. Some have turned to automation, while others focus on improving efficiency.
3. Sustainability
Environmental concerns are pushing fast food chains to adopt more sustainable practices. This includes reducing waste, sourcing ingredients responsibly, and minimizing their carbon footprint.
Despite these challenges, fast food continues to thrive as a retail sector. By embracing innovation and staying ahead of trends, the industry remains a dominant force in the retail world.
Future Trends in Fast Food Retail
As we look to the future, several trends are shaping the fast food retail landscape:
1. Technology Integration
From AI-powered ordering systems to robotics in kitchens, technology is revolutionizing the fast food industry. These advancements promise to enhance efficiency and improve the customer experience.
2. Customization
Consumers today demand personalized experiences, and fast food chains are responding by offering customizable menus. Whether it’s choosing your own toppings or creating a unique sandwich, customization is the way forward.
3. Digital Transformation
The shift to digital platforms is accelerating, with more fast food brands investing in mobile apps and online ordering systems. This trend is expected to continue, driven by the convenience it offers to customers.
By embracing these trends, fast food retailers can stay competitive and meet the evolving needs of their customers.
Conclusion: Is Fast Food Considered Retail?
So, is fast food considered retail? The answer is a resounding yes. Fast food fits perfectly into the retail model, offering products and services directly to consumers. Its success as a retail sector is a testament to its ability to adapt and innovate in response to changing market conditions.
As we’ve explored in this article, fast food’s impact on the economy, its unique characteristics, and its challenges all highlight its importance in the retail landscape. Whether you’re a fan of burgers or tacos, there’s no denying the role fast food plays in our daily lives.
Now it’s your turn. Share your thoughts in the comments below. Do you think fast food deserves its place in the retail world? And don’t forget to check out our other articles for more insights into the fascinating world of retail!
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is Retail?
- Fast Food: The Retail Powerhouse
- How Does Fast Food Fit Into the Retail Landscape?
- Is Fast Food Retail Different From Other Retail Sectors?
- The Economic Impact of Fast Food as Retail
- Challenges Facing Fast Food as Retail
- Future Trends in Fast Food Retail
- Conclusion: Is Fast Food Considered Retail?
- Communism Vs Marxism A Deep Dive Into The Core Differences
- Matthew Gray Gubler Movies A Dive Into The Iconic Roles Of A Hollywood Gem
A Short Overview of the US Fast Food Restaurant Industry

Food service vs retail How do they differ?

The 10 Best Fast Food Brand Logos Designboyo